How to Improve Eye Health Naturally With Vitamin A
Aira
on
April 14, 2023
How to Improve Eye Health Naturally Using Vitamin A

Vitamin A is an essential fat-soluble nutrient that helps
Other benefits of Vitamin A include stimulating the production and activity of white blood cells, remodeling bones, and regulating reproductive cell growth and division. Some people are genetically predisposed to absorb Vitamin A faster and more efficiently than others. If you want to know more about your body’s ability to absorb Vitamin A and other nutrients, a DNA test for vitamin deficiency might be your best option. not just with boosting the body’s immune system but also helps maintain good eye health. Beta-carotene, carrot’s main nutrient, is a precursor to vitamin A.
Other benefits of Vitamin A include stimulating the production and activity of white blood cells, remodeling bones, and regulating reproductive cell growth and division. Some people are genetically predisposed to absorb Vitamin A faster and more efficiently than others. If you want to know more about your body’s ability to absorb Vitamin A and other nutrients, a DNA test for vitamin deficiency might be your best option.
The Connection Between Vitamin A and Eye Health
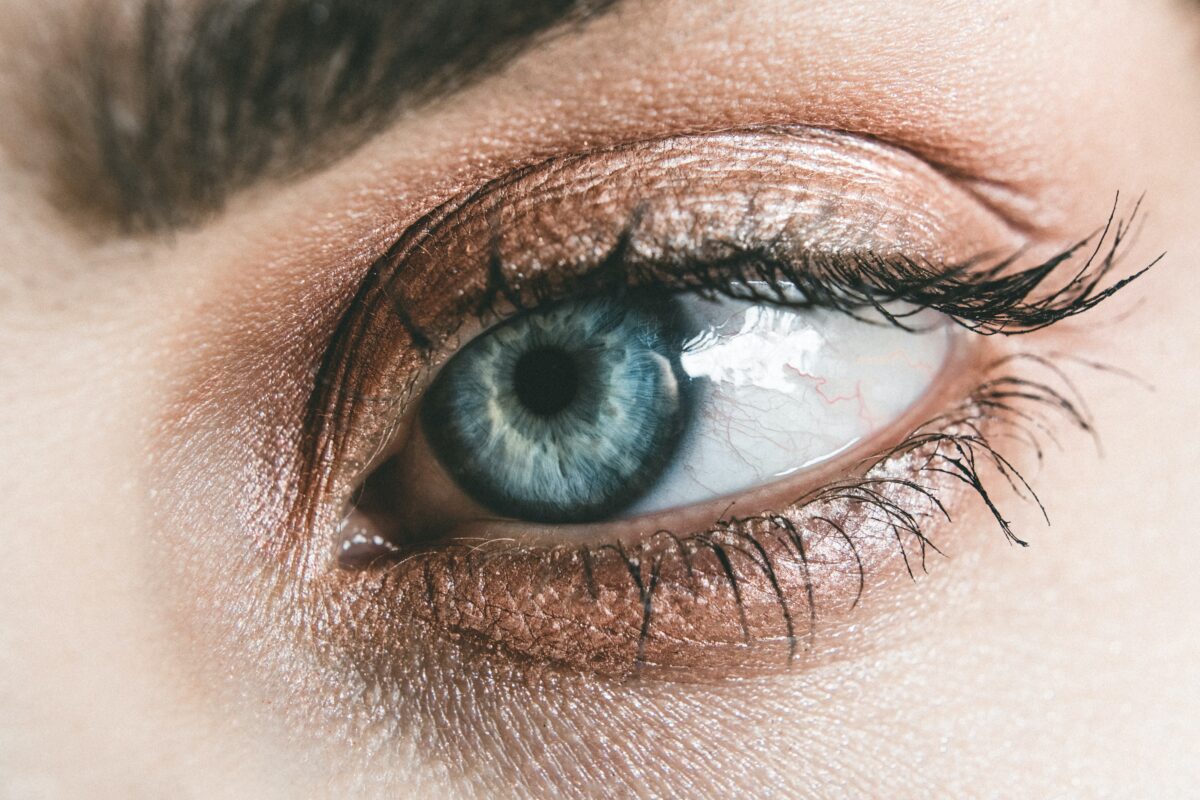
While consuming ample amounts of Vitamin A will not give you night vision or cure your eyes from needing prescription glasses, it has been proven that this vitamin can aid in preventing certain eye conditions. It plays a vital role in eye health by making sure your corneas, the outside covering of your eyes, are always clear.
Vitamin A is also a component of rhodopsin, a protein found in your eyes that helps your vision adjust in low-light conditions. Vitamin A may also help protect against certain eye infections and problems. Some studies even suggest that Vitamin A has the potential to reduce the risk of developing cataracts later on in life. Some superfoods that are rich in Vitamin A are sweet potatoes, leafy green vegetables, pumpkin, and bell peppers.
The first detectable sign of Vitamin A deficiency is usually night blindness or not being to see at all in low-light conditions. The eyes will typically adjust to any dark space as long as even a fraction of light is present. However, people with dangerously low Vitamin A levels will not be able to see at all in the dark. Want to know your Vitamin A levels based on DNA? Try LifeDNA today.

Other Genetic Traits for Eye Health
While consuming ample amounts of Vitamin A will not give you night vision or cure your eyes from needing prescription glasses, it has been proven that this vitamin can aid in preventing certain eye conditions. It plays a vital role in eye health by making sure your corneas, the outside covering of your eyes, are always clear.
Vitamin A is also a component of rhodopsin, a protein found in your eyes that helps your vision adjust in low-light conditions. Vitamin A may also help protect against certain eye infections and problems. Some studies even suggest that Vitamin A has the potential to reduce the risk of developing cataracts later on in life. Some superfoods that are rich in Vitamin A are sweet potatoes, leafy green vegetables, pumpkin, and bell peppers.
The first detectable sign of Vitamin A deficiency is usually night blindness or not being to see at all in low-light conditions. The eyes will typically adjust to any dark space as long as even a fraction of light is present. However, people with dangerously low Vitamin A levels will not be able to see at all in the dark. Want to know your Vitamin A levels based on DNA? Try LifeDNA today.
Genetic Testing for Vitamin Deficiency
Vitamin A is getting more popular as part of people’s daily health routine. It not only helps boost the immune system but also gives the benefit of improving your eye health. The bioavailability of this vitamin varies depending on many factors such as your body’s ability to absorb it, your diet, and your lifestyle.
If you are considering using eye supplements to improve vision, you can include Vitamin A in your list after consulting with your primary care doctor. Get started on your health journey today and find out how your DNA can affect the vitamin and mineral levels in your body. Start with LifeDNA today.
*Understanding your genetics can offer valuable insights into your well-being, but it is not deterministic. Your traits can be influenced by the complex interplay involving nature, lifestyle, family history, and others.
Our reports have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. The contents on our website and our reports are for informational purposes only, and are not intended to diagnose any medical condition, replace the advice of a healthcare professional, or provide any medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Consult with a healthcare professional before making any major lifestyle changes or if you have any other concerns about your results. The testimonials featured may have used more than one LifeDNA or LifeDNA vendors’ product or reports.